Food and the Future Environment

Credit: Green Terraced Rice Field by Joney, licensed through Shutterstock, Used with permission.
Resource Description
The Future of Food is an introductory-level science course that emphasizes the challenges facing food systems in the 21st century, and issues of sustainability for agriculture and other food production activities, as well as the challenges posed by food insecurity and modern diets to human health and well-being. Topics covered include introduction to the coupled-system perspective, historical development of food systems, socioeconomic aspects of the food system, interaction of the food system with the Earth's environment including soil, water, biota and climate, and the future of the food system considering potential changes such as in climate, urbanization, and demography. Learn moreGeographic Foundations of Geospatial Intelligence

Credit: Group of People Enjoying Music Concert by Leah Kelley is free to use
Resource Description
A good detective or researcher like Sherlock Holmes knows the fundamental questions that need to be answered to gather facts to solve a problem. So how does geospatial intelligence contribute to answering these questions? While geospatial technology is useful in revealing who, what, when, and where events take place, it is less useful in explaining why events occur. However, geospatial intelligence analysis leverages geographic information science and technology with the intelligence tradecraft to develop products that support decision-making in national and homeland security, law enforcement, emergency management, and international relief efforts. GEOG 882 will challenge you to think critically, consider alternative viewpoints, and question your own assumptions when analyzing why human events occur over place and time. Learn moreGeographic Information Analysis
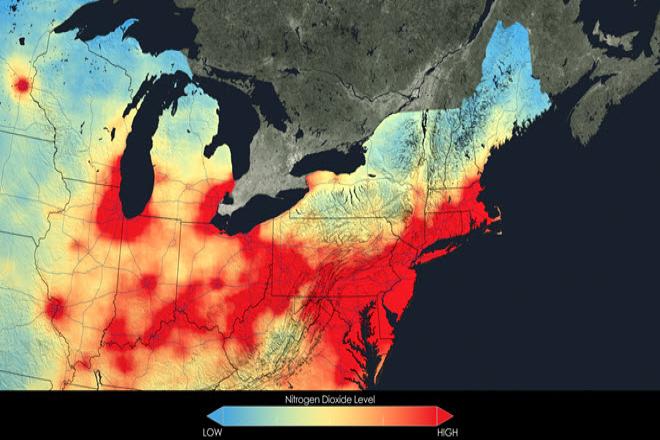
Credit: Close up of nitrogen dioxide in the Northeast U.S. averaged over 2005 by NASA is free to use.
Resource Description
In this data rich world, we need to understand how things are organized on the Earth's surface. Those things are represented by spatial data and necessarily depend upon what surrounds them. Spatial statistics provide insights into explaining processes that create patterns in spatial data. In geographical information analysis, spatial statistics such as point pattern analysis, spatial autocorrelation, and spatial interpolation will analyze the spatial patterns, spatial processes, and spatial association that characterize spatial data. Understanding spatial analysis will help you realize what makes spatial data special and why spatial analysis reveals a truth about spatial data. Learn moreGeography of Water Resources

Credit: Landscape, Water, River, Sky, Lake 2239074 by Alexeev Alexey is licensed under CC0
Resource Description
Geography 431 is designed to further understanding of the natural processes of aquatic ecosystems, management of water resources, and threats to sustaining water quantity. Develop awareness and appreciation of the perspectives about water as a precious resource, commodity, and sometimes hazard. Learn how and why water is distributed unevenly around the Earth. Examine how resource management decisions are strongly related to water availability, quantity, and quality. The course examines water resources management; dams and dam removal; provision of safe potable water; threats to water quantity and quality; land use changes; the water economy; water laws and policy; institutions for water management at the global, national, regional, and local scale; and issues of water security and climate change. Learn moreGeospatial System Analysis and Design
Credit: GEOSPATIAL DATA: Progress Needed on Identifying Expenditures, Building and Utilizing a Data Infrastructure, and Reducing Duplicative Efforts, from the U.S. GAO report, 2015 is Public Domain
Resource Description
Geospatial System Analysis and Design surveys the process of GIS design through critical reading/writing and collaborative discussion. Key topics in the course outline the broad range of current GIS systems, how they are designed and evaluated, and how emerging technologies may impact their design and implementation in the near future. In particular, students will develop a term-long project where they propose a realistic problem scenario that requires the skills and understanding required to effectively complete a geospatial system specification, design, and implementation. Students completing this course are able to develop a comprehensive system design plan that takes into account current technologies as well as emerging technology trends. Learn moreGeospatial Technology Project Management

Credit: Time-lapse Photography of Vehicle Lights by Kaique Rocha is free to use
Resource Description
In GEOG 871, we'll take a critical look at geospatial project management. Project management is a broad discipline that encompasses technical methods such as system design and analysis and also interpersonal factors that affect professional relationships. Project management is also a discipline that has matured outside of, but can be incorporated into, geospatial technology. By the end of this course, you'll have devised a project plan from a scenario built upon a real-life project involving the city of Metropolis geodatabase. We'll work through each of the components in an organized and logical manner and will incorporate constructive peer review to help everyone achieve the best product possible. Learn moreGIS Analysis and Design

Credit: Architectural, design, architecture buildings 425053 by Juhasz Imre is licenced under CC0
Resource Description
Geography 468 provides the geospatial information system professional an overview of systems analysis and design with emphasis on the concepts behind the process, including: business use case modeling, business object modeling, requirements definition, analysis and preliminary design, and, finally, detailed design. The concepts of the geospatial software and database development process are introduced and the current modeling techniques are addressed within the geospatial systems development paradigm. In a series of related activities, students learn about the methods, tools, and concepts of the systems development process to document a portion of a geospatial system with Unified Modeling Language (UML), the standard graphical notation for modeling application needs. Learn moreGIS Programming and Software Development

Credit: High Angle View of Residential Buildings by Palo Cech is free to use
Resource Description
Bill Gates is credited with saying he would "hire a lazy person to do a difficult job" with the justification that "a lazy person will find an easy way to do it." GEOG 485 doesn't teach the lazy way to get the job done, but it does teach the scripting way — which is arguably even better. You've probably heard the "give a fish"/"teach to fish" saying? That's the gist of GEOG 485: to equip you, in an ArcGIS context, with the ModelBuilder and Python scripting skills to make your boring, repetitive geoprocessing tasks easier, quicker and automatic — so you can focus on the more interesting (potentially more valuable) work that you (and your employers) really want you to be doing. Learn moreHuman Use of the Environment

Credit: Green 2558976 by StockSnap is licensed under CC0
Resource Description
Geography 430 is an active, creative learning community focused around understanding the changing relationships between people and their environments, the causes and consequences of environmental degradation, strategies for building a more sustainable world, and the methods and approaches that scholars have used to understand human-environment interactions. The primary course objectives are to help geographers, earth scientists, and other professionals to deepen their appreciation for the complexity of human-environment systems and to develop skills that allow them to interpret, analyze, and communicate effectively regarding human-environment interactions in their lives as students, professionals, and citizens. Learn moreIndependent Study in Geospatial Intelligence

Credit: Computer Laptop by Rudy and Peter Skitterians is licensed under CC0
